19th June 2016 marks the 450th birthday of King James I and VI of England and Scotland. Unification between the two countries, though at times strained, was brought about by James ascending the throne of England in 1603. The unification was the result of one hundred years of Tudor politics.
Back in 1503, Henry VII arranged for his eldest daughter, Margaret Tudor, to marry James IV of Scotland. Margaret during the course of the marriage gave birth to the future James V in 1512. Fighting between Scotland and England resumed. In 1523, Henry VIII attempted to unite the thrones of Scotland and England by offering his daughter, Princess Mary, as a bride for James V. This proposal was rejected. Moving forward several years, James V married the French Mary of Guise in 1538. Henry VIII had lost his third wife in October 1537 and was seeking a new bride. James V beat his uncle, Henry VIII, who was also trying to marry Mary of Guise. In 1541, James V's mother and Henry VIII's sister, Margaret Tudor, passed away; this effectively ended the nearly thirty-year truce between Scotland and England. A war broke out, which saw the death of James V due to illness and depression of the current state of war in December 1542.
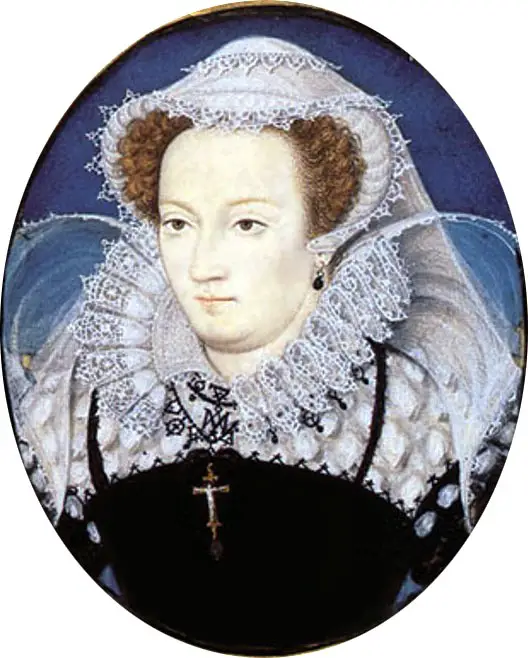
James V and Mary of Guise had one surviving child; namely, Mary, Queen of Scots. She was born in December 1542, and six days later, became Queen of Scots when her father died. Henry VIII sought to have his only legitimate son, the future Edward VI, enter into marriage with the Queen of Scots. During a period from 1543 to 1551, known as the "Rough Wooing", Henry, then Edward VI via the Lord Protector, made serious attempts at trying to force Scotland into agreeing to the proposed marriage between Mary and Edward. Mary was sent to France in 1548 to be raised at the French court and eventually marry the Dauphin. Through a series of unfortunate events, Mary found herself back in Scotland and desirous of a husband by 1565. She married her cousin Henry Stewart, Lord Darnley, and gave birth to the future James I & VI in 1566.
After Mary, Queen of Scots was captured at the Battle of Carberry Hill in June 1567, she was forced to abdicate and by July 1567, the thirteen-month-old James had been proclaimed King of Scots. James had a very difficult upbringing. He was routinely disciplined and over-worked by his tutor, George Buchanan. Scotland had seen five different regents by 1578. In 1582, the young James was kidnapped during the Raid of Ruthven. Dressed in disguise, James managed to slip away from Ruthven in 1583. He fled to St. Andrews and proclaimed himself King.
Not unlike England, Scotland was facing trouble due to struggles between the Catholic and Protestant factions. Interestingly, James also had a fascination with witchcraft during his lifetime. Ultimately, James wished to be a "universall King", and despite his Protestant leanings, did not treat the rebellious Catholic Earls harshly. Maintaining his status as a Protestant ruler was beneficial to James, too, as it kept him in the good graces of his unmarried, child-free cousin, Elizabeth I of England. As the great-grandson of Margaret Tudor, James had a hereditary claim to the throne of England. He was careful not to vex Elizabeth I about his partially Tudor pedigree; perhaps James learned through the ostentatious mistakes made during his mother's life that openly pressing his claim to the Throne of England was not the best way to ascend that throne.James did manage an alliance with England in 1585, two years before his mother was beheaded for plotting against Elizabeth I. Upon learning of Mary, Queen of Scots' execution, James simply made a short political protest, and that was all. He did start corresponding with Robert Cecil, Elizabeth I’s Secretary, a friendship that would prove to be invaluable upon Elizabeth I’s death.
In 1589, it was time for the King of Scotland to find his queen. James chose the Protestant Anne of Denmark, and set off for Oslo to retrieve her, Anne's fleet having been forced back to the Norwegian coast. Distressed by the poor state of Scotland's Exchequer and concerned for making a good impression upon his new wife, James wrote to one of his wealthier ministers, "For God's sake, take all the pains ye can to tune our folks well now against our homecoming lest we be all shamed before strangers. Thus recommending me and my new rib* to your daily prayers, I commit you to the only All-sufficient."
During James's early reign in Scotland, there were two issues: which form the Reformed Church of Scotland would take, and the formation of the Presbyterian Church. Subsequently, these developments in religion provided another source of difficulty. The Reformed Church came about in stark contrast to the development of the Reformed Church of England; Henry VIII forced the formation of the Reformed Church to meet his own needs, whereas the Reformed Church of Scotland was developed without the wishes of Scotland's here-to-fore Catholic monarchs. Overall, James was more in favor of episcopacy, and was against the Church interfering with matters of the State. However, James was more tolerant than not.
James became King of England upon the death of Elizabeth I in March of 1603, 100 years after Elizabeth's aunt, Margaret Tudor, had married James IV in an effort to unify, or at least bring peace to, England and Scotland. Though James V, nephew to Henry VIII and son to Margaret Tudor, perhaps spurned his uncle by marrying Marie of Guise, Henry was still open to a marriage alliance. Henry offered his daughter Mary as a bride to his nephew, James V of Scotland. Henry tried his best to force the marriage of his own son, Edward, to Mary, Queen of Scots. Mary was Henry's great-niece. The Queen of Scots asserted her claim to the English throne, at times more loudly than others, throughout her life, though she never could attain it. Neither Mary I of England, nor Edward VI, nor Elizabeth I managed to secure a marriage with their neighbours to the north. But, the careful, conscientious behaviour of King James VI of Scotland, whose great-great-grandfather was the first Tudor monarch, Henry VII of England, saw to it that a Tudor truly did sit on the throne of both England and Scotland, even if it took 100 years for the Tudors to get there.
*What a way to refer to one's new wife!
Heather R. Darsie lives in the United States with her family and three parrots. She works in the legal field, with a focus on children. She obtained a Bachelor of Arts degree in German Languages and Literature, then a Juris Doctorate in American jurisprudence, and studied abroad in Costa Rica and France. Heather has always loved history. She first became acquainted with Elizabeth I when she was in middle school and chose to write a book report about her. Since then, she has always held an interest in the Renaissance and its numerous enigmatic citizens, with particular focus on the history of England and Italy. She is currently working on a book on the heraldry of Tudor women and is also researching Anne of Cleves.
Sources and Suggested Reading
- Maclean, Fitzroy. A Concise History of Scotland. London: Thames and Hudson. 1970.
- History Learning Site. “Henry VIII and Scotland.” http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/tudor-england/henry-viii-and-scotland/ Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- Hanson, Marilee. "King Edward VI Tudor Monarchs Facts & Biography". February 1, 2015, http://englishhistory.net/tudor/monarchs/king-edward-vi/ Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- Education Scotland. “Marie de Guise (1515-1560). http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/scotlandshistory/renaissancereformation/mariedeguise/index.asp Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- Lee, Maurice. Great Britain's Solomon: James VI and I in his Three Kingdoms, Urbana: University of Illinois Press. 1990.




Very well written and enlightening. Thanks very much.
James I & VI was a Stuart, since his mother was a Stuart (Mary Stuart), as was his father (Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley). He’s descended from Tudors, but he’s not technically a Tudor.
Technically, he’s a Stuart and is the first king of the Stuart dynasty on the throne of England, but I think Heather is making the point that he was very much a Tudor. He was descended from the Tudors twice over, in that both his mother and father were descended from Henry VII through Margaret Tudor. An interesting family tree.